Entdecken
Vertiefen Sie Ihr Wissen durch Literatur und wissenschaftliche Dokumentation.
Vertiefen Sie Ihr Wissen durch Literatur und wissenschaftliche Dokumentation.

Vertiefen Sie Ihr Wissen durch Literatur und wissenschaftliche Dokumentation.
key:global.content-type: Artikel
Sichten Sie die klinischen Evidenz, die für die verbesserten Ergebnisse der Anwendung von TAI bei pädiatrischen Patienten spricht, wenn sie mit einem individuellen Ansatz zu Beginn der TAI gekoppelt sind.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Der Einfluss der transanalen Irrigation auf die Darmmikrobiota könnte sich positiv auf das Immunsystem auswirken und zu einer Verringerung von Harnwegsinfektionen beitragen, wie aus dieser klinischen Studie von Futura et. al.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Diese Studie bietet wertvolle Einblicke in die Erfahrungen von Personen, die den IK durchführen, um die Patientenversorgung und -unterstützung zu optimieren.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Klinische Daten zur transanalen Irrigation als Mittel zur Behandlung des neurogenen Darms in der pädiatrischen Population mit Spina bifida

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Artikel fassen wir die wichtigsten Ergebnisse und Empfehlungen einer Studie von Bauer et al. aus dem Jahr 2023 zusammen, die die intermittierende Katheterisierung (IK) bei Kindern und Jugendlichen im schulischen Umfeld untersucht.

key:global.content-type: Publication Highlight
Die traditionelle Sichtweise der Sterilität des Urins wurde durch die Entdeckung des Harnmikrobioms, d. h. einer Mischung aus Bakterien und Mikroorganismen in den Harnwegen, in Frage gestellt. Diese einzigartige Beziehung zwischen Mikroben und Menschen ist noch nicht vollständig verstanden, hat aber in den letzten zehn Jahren in der klinischen Forschung viel Aufmerksamkeit erregt.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Publikations-Highlight können Sie über eine Studie über chronische idiopathische Verstopfung bei Kindern lesen und darüber, wie eine Darmspülung, auch transanale Irrigation (TAI) genannt, die Selbstständigkeit verbessern und die Symptome reduzieren kann.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Eine Harnröhrenstriktur ist eine krankhafte Verengung der Harnröhre und wird häufig durch ein Trauma oder eine Entzündung verursacht. Da die Katheterisierung eine Ursache für Strikturen ist, sind die nicht-traumatische Katheterisierungstechnik und das Kathetermaterial wesentliche Bestandteile, um das Auftreten dieser Komplikationen zu verhindern.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In mehr als 40 Jahren auf dem Markt wurde LoFric auf verschiedene Weise eingesetzt und dokumentiert. Neben der effizienten Entleerung der Blase umfasst der vielseitige Einsatz von LoFric die Behandlung und Vorbeugung von wiederkehrenden Strikturen, die Verabreichung einer Chemotherapie durch Instillation der Blase und die Lösung seltener Komplikationen.

key:global.content-type: Publication Highlight
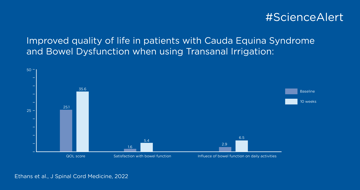
In diesem Publikations-Highlight können Sie nachlesen, wie Sie Darmfunktionsstörungen bei Personen mit Cauda-equina-Syndrom behandeln können.
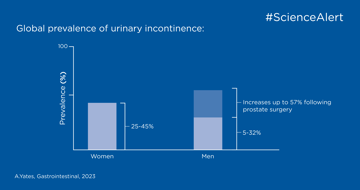
In diesem Publikations-Highlight können Sie über die Erkennung, Beurteilung und Behandlung von Harninkontinenz und Darmkontrollproblemen lesen.
Es kann überwältigend sein, auf dem Laufenden zu bleiben und den Wahrheitsgehalt von wissenschaftlichen Artikeln und klinischen Studien zu bestimmen, daher haben wir eine Checkliste zusammengestellt, die Ihnen helfen kann.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In dieser wissenschaftlichen Übersichtsarbeit erfahren Sie mehr über Ursachen und Behandlung der unvollständigen Stuhlentleerung.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Publikations-Highlight können Sie mehr über die Ursachen, Auswirkungen und Behandlung von Verstopfung bei Kindern lesen.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Publikations-Highlight können Sie nachlesen, was ein neurogener Darm ist und welche Ziele und Empfehlungen es für die Behandlung gibt.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Dies ist ein Publikationshighlight des Artikels Langzeitwirksamkeit und Sicherheit der transanalen Irrigation bei Multipler Sklerose von Passananti et al. 2016

key:global.content-type: Artikel
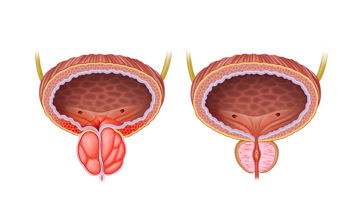
Die benigne Prostatahyperplasie (BPH) ist eine der häufigsten Diagnosen bei Männern. Etwa 100.000 Männer werden jedes Jahr mit einer transurethralen Prostataoperation (TURP) behandelt, was sie zu einem der häufigsten chirurgischen Eingriffe in den Vereinigten Staaten und mehreren anderen Ländern macht.
key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Publikations-Highlight erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie Sie neurogene Blasen- und Darmfunktionsstörungen mit einem patientenzentrierten Instrument, der Zielerreichungsskalierung (GAS), bewerten können, um das Management zu individualisieren.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Das Blasenmanagement mit intermittierender Katheterisierung ist mit Komplikationen verbunden. Die schwerste und häufigste ist die Harnwegsinfektion.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Für diejenigen, die ihre Blase nicht auf normale Weise entleeren können, ist die intermittierende Katheterisierung die Therapie der Wahl, um die Gesundheit der Harnorgane zu erhalten.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Die Blaseninstillation wird zur lokalen Verabreichung von Medikamenten in die Blase verwendet. Dies wird zum Beispiel zur Behandlung von interstitieller Zystitis und Krebs eingesetzt. Die Medikamente werden über einen Katheter verabreicht, und eine hydrophil beschichtete Oberfläche wie die der LoFric-Katheter reduziert das Risiko für Traumata im Zusammenhang mit der Instillationstherapie.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Bei Wellspect HealthCare nehmen wir unsere Verantwortung für die Umwelt ernst. Wir arbeiten kontinuierlich daran, die Umweltauswirkungen unserer Produkte zu minimieren.
key:global.content-type: Artikel
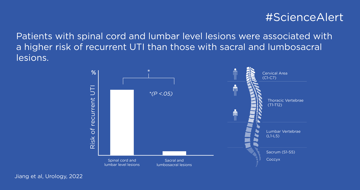
Wiederkehrende Harnwegsinfektionen bei Kindern mit neurogener Blasenfunktionsstörung stellen ein hohes Risiko für schwere Nierenschäden dar und müssen beachtet werden. Diese Studie ist nützlich, um Behandlungen und proaktive Maßnahmen zur Vorbeugung wiederkehrender Harnwegsinfektionen zu bestimmen.
key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Publikations-Highlight können Sie nachlesen, wie sich Verstopfung auf urogenitale Symptome bei Frauen auswirkt.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
In diesem Publikations-Highlight erfahren Sie mehr über autonome Dysreflexie (AD) und wie Sie mit einer AD-Episode umgehen können.

key:global.content-type: Artikel

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Urin hat oft eine hohe Konzentration an Partikeln und einen geringen Wassergehalt. Dies wird als hohe Osmolalität bezeichnet. Die Osmolalität des Urins hat einen direkten Einfluss auf die Katheteroberfläche und spielt eine wichtige Rolle für Menschen, die hydrophile Katheter verwenden. Katheter mit einer Oberflächenosmolalität im Gleichgewicht mit dem Urin sind der Schlüssel zur Verringerung der Rückzugsreibung.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Umfangreiche Studien stützen die wissenschaftliche Literatur, die behauptet, dass die Verwendung von hydrophilen Kathetern Harnröhrentraumata und Harnwegsinfektionen reduziert. Dies wiederum kann den Einsatz an Antibiotika minimieren. Aufgrund dieser Vorteile wissen wir heute, dass hydrophile Katheter eine der kostengünstigsten Möglichkeiten sind, um langfristige urologische Komplikationen im Allgemeinen und Harnwegsinfektionen im Besonderen zu verhindern.
key:global.content-type: Artikel
Ein hydrophiler Katheter wird empfohlen, um Schäden an der Harnröhre zu reduzieren und das Risiko einer Hämaturie, die eine häufige Komplikation ist, zu senken. Eine Cross-over-Studie, in der verschiedene hydrophile Katheter verglichen wurden, zeigte eine noch geringere Hämaturiehäufigkeit bei Patienten, die sich für LoFric entschieden.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Die Adhärenz des Patienten spielt eine Schlüsselrolle für eine erfolgreiche (und kostengünstige) Katheterbehandlung. Ein Patient, der sich als Teil der Entscheidungsfindung fühlt, die Kontrolle über seine Optionen hat und wie sie mit seinem Lebensstil zusammenarbeiten, ist eher geneigt, bei seiner Therapie zu bleiben und anschließend ein gutes klinisches Ergebnis zu erzielen.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Die Einführung eines berührungslosen Katheters/einer Technik für die intermittierende Katheterisierung scheint sowohl von Pflegekräften als auch von Patienten gut akzeptiert zu werden und ist nicht unbedingt mit höheren Kosten verbunden. Im Gegenteil, es könnte potenziell Kosten senken, Zeit und Fehler im Gesundheitssystem sparen und Infektionskomplikationen im Allgemeinen reduzieren. Die klinische Evidenz für die Verwendung der berührungslosen Technik/Katheter zur Reduzierung von Harnwegsinfektionen ist gering, aber die derzeit verfügbaren Studien deuten auf Vorteile hin.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Zusammenfassung der ersten Daten zu Navina Smart
key:global.content-type: Artikel
Catheter associated urinary tract infections (CAUTI) are common in the hospital setting with consequential morbidity and mortality. The risk of bacterial adhesion and invasion of the urinary tract increases with use of an indwelling catheterization and may be reduced by adopting intermittent catheterization using hydrophilic single-use catheters.

key:global.content-type: Artikel

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Die verfügbare klinische Evidenz unterstützt die Strategie, die intermittierende Katheterisierung immer als erste therapeutische Wahl in Betracht zu ziehen, bevor die Verwendung eines Dauerkatheters (via Harnröhre oder suprapubischen Katheter) in Betracht gezogen wird. Die intermittierende Katheterisierung ist von zentraler Bedeutung, um die Morbidität im Zusammenhang mit Nierenversagen und neurogener Blasenfunktionsstörung zu reduzieren.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Eine überraschend hohe Anzahl von Patienten verwendet täglich Katheter, die für den einmaligen Gebrauch bestimmt sind, und setzt sie dem Risiko unnötiger Komplikationen aus. Hydrophile Einwegkatheter für die intermittierende Katheterisierung senken das Risiko für kurz- und langfristige Komplikationen und sind für viele Patienten eine bequeme und bevorzugte Wahl.
key:global.content-type: Artikel
Darmfunktionsstörungen sind von Missverständnissen und Tabus umgeben, die die Behandlung beeinträchtigen und zu einer Selbstmedikation führen können, die nicht immer unschädlich für die Patientenversorgung ist.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
Unter Stuhlinkontinenz (FI) versteht man den unwillkürlichen Verlust von rektalen Inhalten wie festem und flüssigem Stuhl, Schleim oder Blähungen. FI ist keine Diagnose, sondern ein Symptom. Es gilt als stigmatisierende Erkrankung, und die Angst vor einem Vorfall in der Öffentlichkeit schränkt das soziale sowie das berufliche Leben der Betroffenen ein. Obwohl es viele Behandlungsmöglichkeiten gibt, ist ihre Langzeitwirksamkeit nur unzureichend untersucht.

key:global.content-type: Artikel
key:global.content-type: Artikel
key:global.content-type: Artikel
Die transanale Irrigation (TAI) ist eine gut dokumentierte und sichere Darmmanagementtherapie. Heute ist die Compliance das Hauptproblem bei der TAI-Therapie und kann durch ein besseres Wissen darüber, welcher Patient am besten von der TAI profitiert, verbessert werden. Patientenschulungen und eine engmaschige Nachsorge mit digitaler Unterstützung während der Eingewöhnung können ebenfalls die Compliance erhöhen.
